Introduction
Agar aap ek expert web developer ho, to aap already jaante ho ki login system kisi bhi dynamic website ka backbone hota hai. Chahe wo CMS ho, e-commerce ho, ya custom SaaS product — security compromise ka matlab hota hai pura system risk me.
Is tutorial me hum PHP 8.4 ka use karke ek secure, scalable aur performance-optimized login system build karenge jisme:
- Passwords plain text me kabhi store nahi honge
- Password hashing & verification best practices follow hongi
- PDO + Prepared Statements SQL Injection se protect karenge
- Common developer mistakes aur unke solutions discuss honge
- Performance optimization ke real-world tips milenge
Language Hinglish rakhi gayi hai taaki Indian developers easily follow kar saken, bina concepts dilute kiye.
Prerequisites
Tutorial start karne se pehle ensure karein:
Technical Requirements
- PHP 8.4+
- MySQL / MariaDB
- Apache / Nginx server
- Basic knowledge of:
- PHP syntax
- MySQL queries
- HTML forms
Recommended PHP Extensions
pdopdo_mysqlopenssl
Understanding Password Hashing (Before Coding)
Bahut se beginners abhi bhi ye galti karte hain:
password = '123456'
Aur directly database me save kar dete hain. Ye major security flaw hai.
Why Password Hashing?
- Hash ek one-way function hota hai
- Original password wapas nahi nikala ja sakta
- Agar database leak bhi ho jaye, passwords safe rehte hain
PHP me hum use karte hain:
password_hash()password_verify()
Ye internally bcrypt / argon2 jaise strong algorithms use karta hai.
Database Structure (User Table)
Sabse pehle ek clean aur optimized users table banate hain:
CREATE TABLE users (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR(150) NOT NULL UNIQUE,
password VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
) ENGINE=InnoDB;
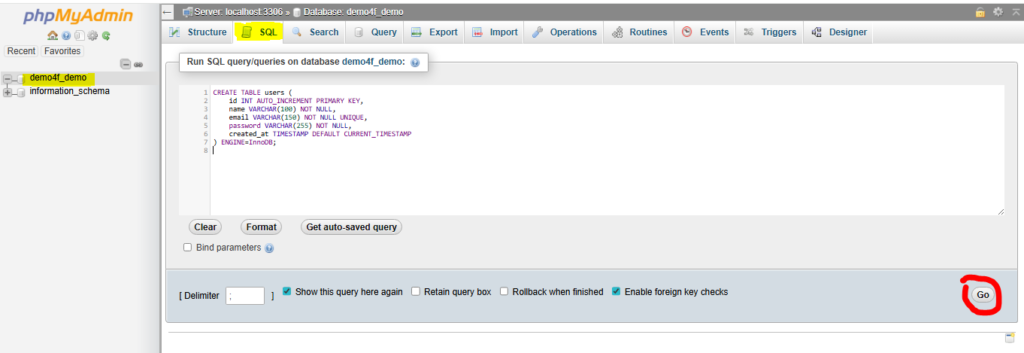
Explanation
password VARCHAR(255)
Kyunki hashed password length zyada hoti haiUNIQUE email
Duplicate account creation rokne ke liyeInnoDB
Better performance + transactions support
Database Connection (PDO Style)
db.php
<?php
$host = "localhost";
$db = "secure_login";
$user = "db_user";
$pass = "db_pass";
$options = [
PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE => PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION,
PDO::ATTR_DEFAULT_FETCH_MODE => PDO::FETCH_ASSOC,
PDO::ATTR_EMULATE_PREPARES => false,
];
try {
$pdo = new PDO(
"mysql:host=$host;dbname=$db;charset=utf8mb4",
$user,
$pass,
$options
);
} catch (PDOException $e) {
die("Database connection failed");
}
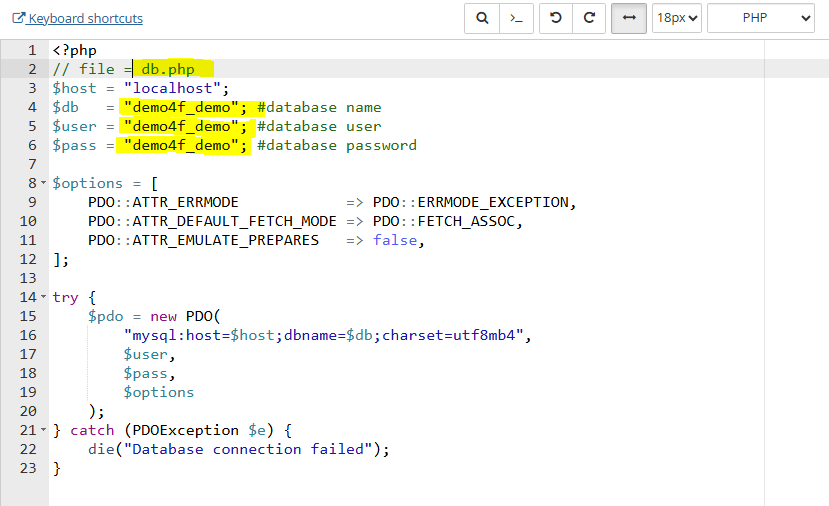
Explanation
ERRMODE_EXCEPTION
Errors ko silently ignore nahi karegaEMULATE_PREPARES = false
Real prepared statements → better securityutf8mb4
Emoji + international characters support
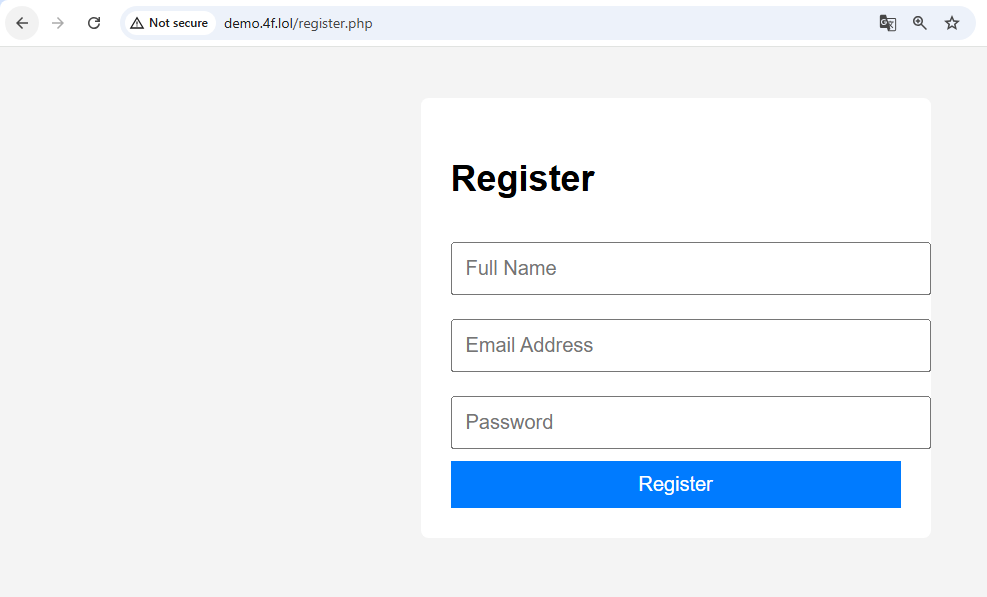
Step 1: User Registration with Password Hashing
register.php (Backend Logic)
<?php
require "db.php";
if ($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] === "POST") {
$name = trim($_POST["name"]);
$email = trim($_POST["email"]);
$pass = $_POST["password"];
if (empty($name) || empty($email) || empty($pass)) {
die("All fields are required");
}
$hashedPassword = password_hash($pass, PASSWORD_DEFAULT);
$sql = "INSERT INTO users (name, email, password) VALUES (?, ?, ?)";
$stmt = $pdo->prepare($sql);
$stmt->execute([$name, $email, $hashedPassword]);
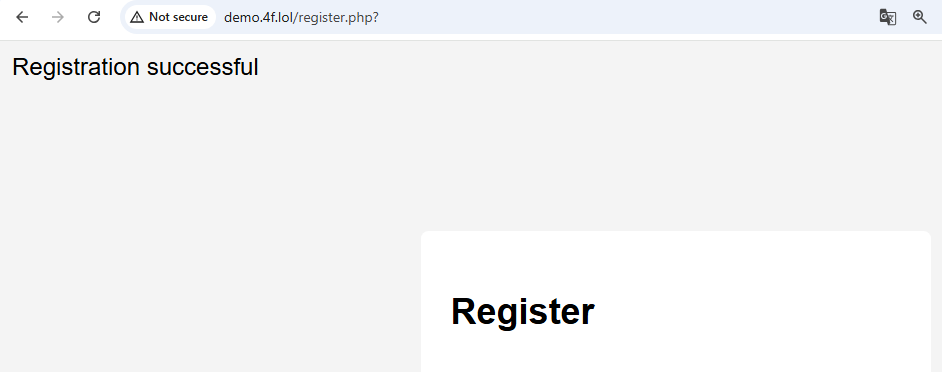
echo "Registration successful";
}
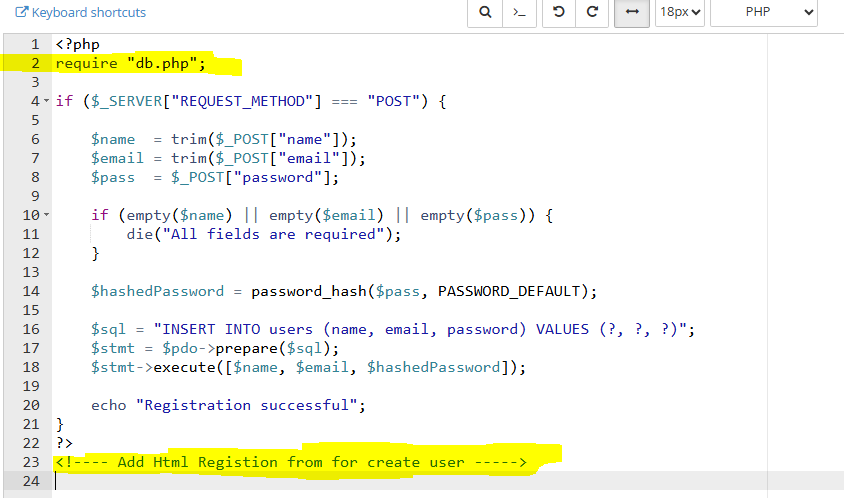
Explanation
trim()
Extra spaces remove karta haipassword_hash()
Automatically best algorithm select karta haiPASSWORD_DEFAULT
Future-proof (PHP updates ke saath improve hota rahega)- Prepared statement
SQL Injection ka koi scope nahi
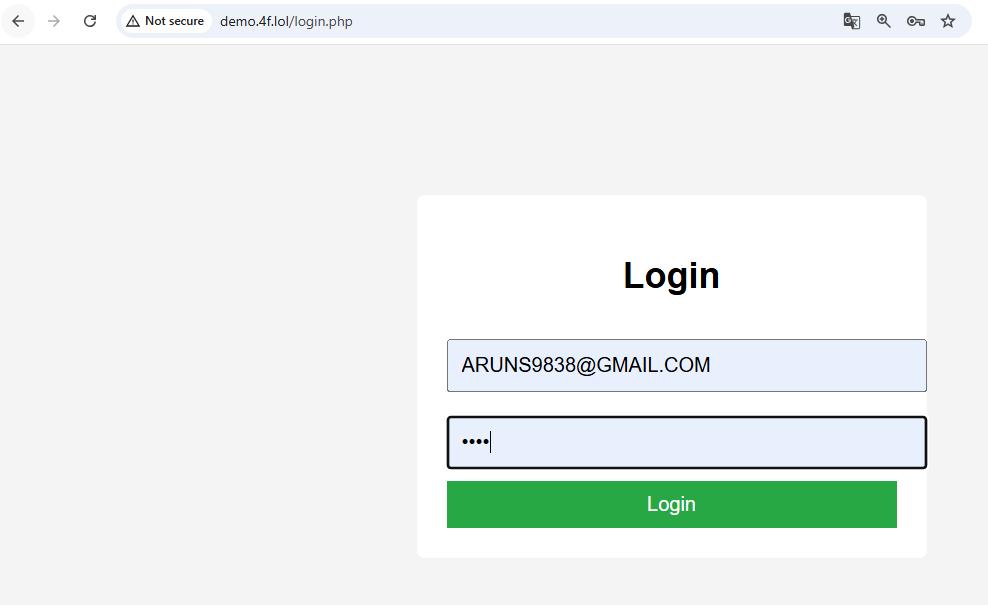
Step 2: Login System with Secure Verification
login.php (Backend Logic)
<?php
require "db.php";
session_start();
if ($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] === "POST") {
$email = trim($_POST["email"]);
$pass = $_POST["password"];
$sql = "SELECT id, password FROM users WHERE email = ?";
$stmt = $pdo->prepare($sql);
$stmt->execute([$email]);
$user = $stmt->fetch();
if ($user && password_verify($pass, $user["password"])) {
session_regenerate_id(true);
$_SESSION["user_id"] = $user["id"];
echo "Login successful";
} else {
echo "Invalid email or password";
}
}
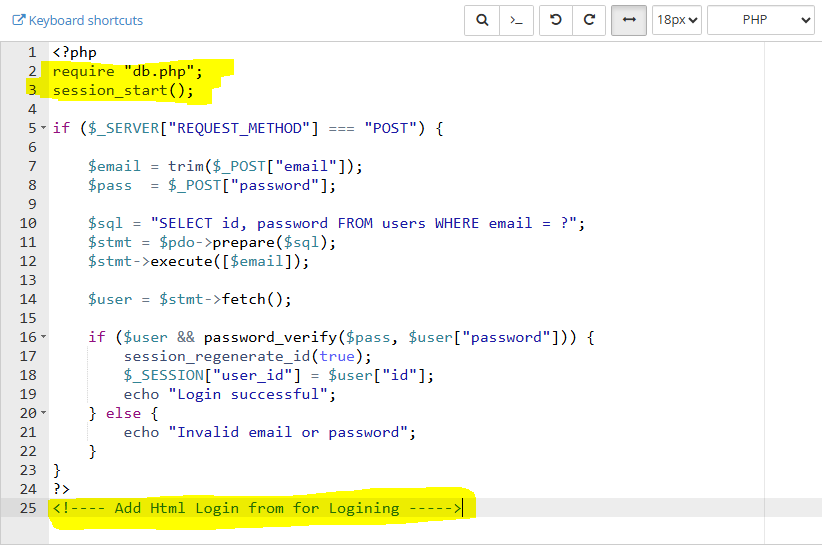
Explanation
password_verify()
Plain password ko hashed password se safely compare karta haisession_regenerate_id(true)
Session fixation attack prevent karta hai- Password mismatch pe exact error nahi bataya
Security best practice
Step 3: Secure Session Handling
Session security often ignore hoti hai, jo dangerous hai.
session_config.php
<?php
ini_set("session.use_strict_mode", 1);
ini_set("session.use_only_cookies", 1);
ini_set("session.cookie_httponly", 1);
ini_set("session.cookie_secure", 1); // HTTPS required
Explanation
httponly
JavaScript session access nahi kar saktasecure
Sirf HTTPS pe session cookie send hoti haistrict_mode
Fake session IDs reject karta hai
Demo Login
Comment Blow i am update this file link in zip
Common Errors & Solutions (Developer Problems)
❌ “Password_verify always returns false”
Reason:
- Plain password ko hash karke compare kar rahe ho
Fix:
password_verify($plain, $storedHash);
❌ “Headers already sent” error
Reason:
- Output before
session_start()
Fix:
- Session start sabse upar rakhein
❌ Slow login queries
Reason:
- Email column indexed nahi hai
Fix:
ALTER TABLE users ADD INDEX (email);
Performance Optimization Techniques
1. Database Indexing
- Email column pe index → faster lookup
2. Avoid SELECT *
Sirf required fields fetch karein:
SELECT id, password FROM users WHERE email = ?
3. Password Rehashing Strategy
if (password_needs_rehash($hash, PASSWORD_DEFAULT)) {
$newHash = password_hash($pass, PASSWORD_DEFAULT);
}
Ye ensure karta hai ki old users bhi stronger hash pe move ho jayein.
Extra Security Enhancements (Optional but Recommended)
- Login attempt limiting (brute force protection)
- CSRF token forms me
- 2FA integration (OTP / Email)
- HTTPS enforced via
.htaccess
Conclusion
Is tutorial me humne ek production-ready secure login system build kiya jo:
- PHP 8.4 standards follow karta hai
- Password hashing ke modern rules apply karta hai
- SQL Injection aur session attacks se protect karta hai
- Performance aur scalability ko dhyaan me rakhta hai
Agar aap is structure ko follow karte ho, to aapka login system secure, fast aur future-proof rahega — bina unnecessary complexity ke.